ADVERTISEMENT
When selecting eggs, the source plays a crucial role in their quality. Here’s a look at different types of eggs and how to recognize the healthiest options.
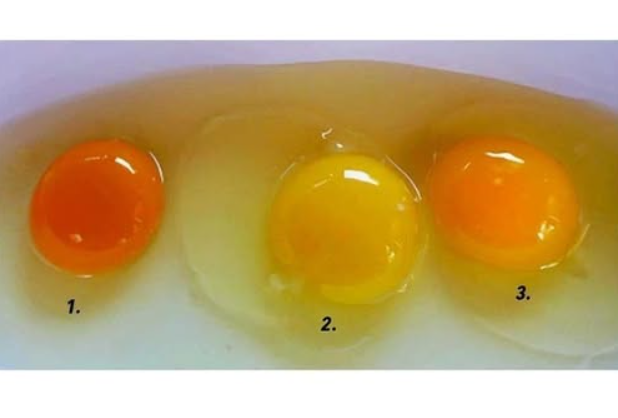
Pastured Eggs – Type #1: The Nutrient Powerhouse
Overview:
Pastured eggs are considered the best quality. Hens raised in pastured environments roam freely, foraging on grasses, insects, and seeds.
- Nutritional Benefits:
- Rich in vitamins A, D, and E, which are vital for immune function and bone health.
- High in omega-3 fatty acids, promoting heart health.
- Color and Quality:
- Dark orange yolks indicate a high level of carotenoids and xanthophylls, antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and support eye health.
- Taste:
- Many people find that pastured eggs have a richer, creamier flavor thanks to the hens’ varied diets.
Caged Eggs – Type #2: The Least Nutritious Option
- Limited Nutrition:
- A basic diet of wheat and corn results in paler yolks and fewer essential nutrients.
- Hens’ Health:
- Poor living conditions increase stress levels, adversely affecting both the hens’ health and the quality of the eggs.
- Color and Quality:
- Pale yellow yolks indicate a lack of dietary diversity and lower nutrient content, including omega-3s and vitamins A and E.
Free-Range Eggs – Type #3: The Middle Ground
Overview:
Free-range eggs come from hens that have more freedom than caged hens, often having access to outdoor spaces while mainly eating grains.
- Moderate Nutrition:
- Free-range hens may occasionally eat insects, resulting in yolks that are darker than those of caged eggs but lighter than pastured ones.
- Healthier Option:
- These eggs typically contain more vitamin A and omega-3 fatty acids compared to caged eggs, making them a solid choice if pastured eggs are not available.
- Taste and Quality:
- Free-range eggs offer a balanced flavor that falls between the richness of pastured eggs and the milder taste of caged eggs.
Nutritional Comparison: Pastured vs. Free-Range vs. Caged Eggs
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT